How Deadlifts Worked In Improving Core Muscle Strength and Stability
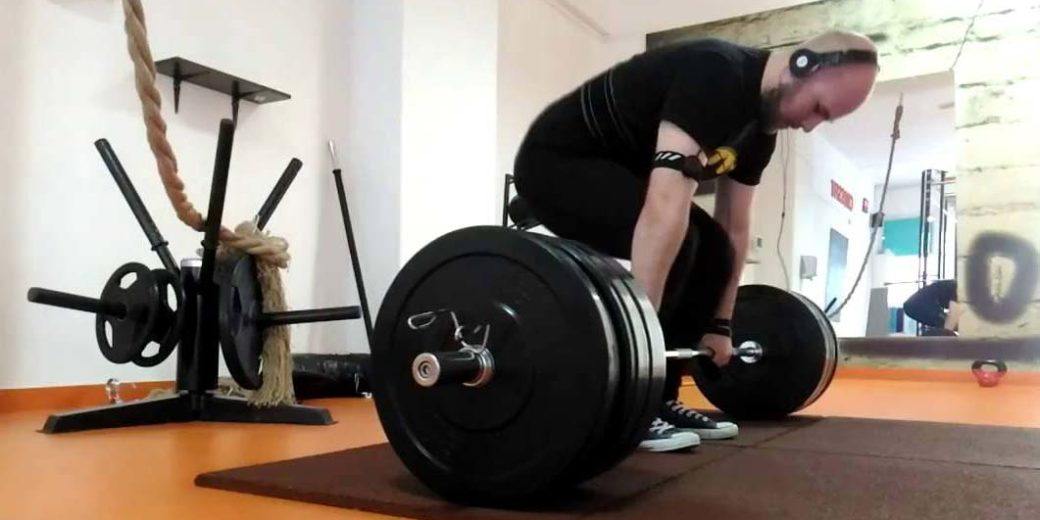

Deadlifts are a staple in any muscle-building regimen, oftentimes accompanied by either cardio or flexibility exercises.
It is also prominently featured in popular culture. The iconic weight-lifter is oftentimes shown to be performing deadlifts or squats.
Oftentimes considered a feat in and on itself to perform. The benefits of the exercise far outweighs the difficulty.
It is considered as one of the top 4 strength exercises, and should be in anyone’s workout planner if you want to increase not just muscle mass but also core muscle strength.
In this article, we are going to go deep into the realm of the deadlifts and show you that this classic workout staple is far from being – dead.
What are Core Muscles and What do they do?
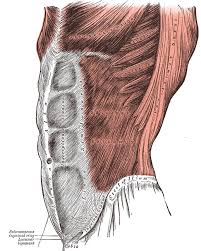
Core muscles are the group of muscles which forms the abdomen.
 The core is considered as the center of gravity and force when working out.
The core is considered as the center of gravity and force when working out.
The strength of core muscles are highly dependent on the type of strength workout.
Having a good amount of core strength is a necessity in various advanced and intermediate exercises as having a weak core oftentimes lead to muscle injury.
Developing the core muscles is essential in not only maximizing the overall capacity of the muscles to resist damage but also in building proper form.
The muscles included in the group includes the Major Core and Minor Core muscles.
Major Core Muscles includes:
- the Pelvic Floor Muscles
- Transversus Abdominis
- Multifidus
- Internal and External Obliques
- Rectus Abdominis
- Erector spinae (sacrospinalis) especially the longissimus thoracis
- Diaphragm
Minor Core Muscles includes:
- The Latissimus Dorsi
- Gluteus Maximus
- Trapezius
The major core muscles in particular are the ones responsible for balancing and stabilizing the force and offering resistance when working out or doing other activities.
The core is responsible for much of the full-body functional movement.
In addition, the core is largely responsible for determining a large part of a person’s posture. The core muscles help align the spine, ribs, and pelvis so it can resist a specific force, whether it is static or dynamic. The minor core muscles on the other hand performs the function of support and cushion.
Static and Dynamic Core Function
Static core function is the ability of the core muscles to align the skeleton so it can resist a force that does not change direction.
An example of static core function in workout routines includes planking.
 When initiating a planking posture, the muscles and the skeleton are continually aligned to resist one type of force – gravity.
When initiating a planking posture, the muscles and the skeleton are continually aligned to resist one type of force – gravity.
Dynamic core function on the other hand refers to the ability of the core muscles to continually align the skeleton to resist force going towards or against the source.
It is easily observed when doing push ups.
As the chests and abdomen are lifted from floor level, the core resists the downward pull of gravity which pushes the body upwards, and as it is pushed down it must resist the rapid acceleration by the downward push by gravity.
Core Stability and Core Strength
It is important to note that core stability and core strength are two different things.
Core stability refers to the ability of the core muscles to stabilize the spinal column during all movements which includes both horizontal and vertical movements such as running or jumping.
 Core Strength however refers to how the core muscles are able to resist or create force. Anatomically the core muscles involved in stability and strength also differs. The muscles responsible in core strength involves the muscles which are superficial or farther from the bone.
Core Strength however refers to how the core muscles are able to resist or create force. Anatomically the core muscles involved in stability and strength also differs. The muscles responsible in core strength involves the muscles which are superficial or farther from the bone.
The muscles responsible for core stability are the deep seated muscles which are much closer to the bone. The difference in location of these two muscles determines how they interact during movement. The superficial muscles of the core which are responsible for strength are highly mobile,
this means they are able to contract and extend, this makes them largely responsible for movement. The deep-seated core muscles on the other hand envelop the skeletal frame which makes them mostly static.
They however still play a large role in movement as they largely resist and counterbalance force which would otherwise cause damage to the bone structure.
How Important are Core Muscles Worked in Deadlifts?
In any workout, having a good form is a crucial turning point to a great workout to that of a disastrous afternoon at the gym.
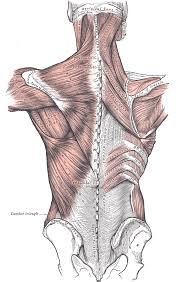
Having a thorough understanding on core strength, core stability, and a good workout form are key to be able to grasped the complexity of a deadlift.
A good form not only matters greatly in the realms of safety, proper muscle development, and deadlifts.
It also reduces the chance of injury and prevents the muscles from being strained too much. It is important to note that having a good form is totally different from just looking good while lifting weights.
Benefits of a Good Form
- Helps muscles develop properly
- Ensures you are using the correct muscles
- Helps Facilitate movement
- Prevents joint, bone, and muscle injury
- Helps in enhancing the muscles aesthetically
- Distributes force evenly
In any workout a good form is necessary but in a deadlift the difference between a good form and a bad one can be very glaring. This is important to discuss as deadlifts just like any type of resistance exercise carries its own set of risks. If done incorrectly it might cause either temporary or permanent damage to the spine, muscles, and the skeleton.
How are Core Muscles Affected by Deadlifts
Deadlifts are a staple in any strength-training exercise and admissibly a part of any bodybuilders pool of exercises.
The reason deadlifts are popular has got to do with how it affects the core muscles similar to its cousin – the squat. Deadlifts in particular target both static and dynamic muscles of the core.
The dynamic core muscles receives resistance through the weights or the pull of gravity which helps it develop. The static core muscles which are found in the deep-seated muscles of the back and the abdomen are developed through a maintaining a neutral spine.
Perfoming Deadlifts and Core Muscles
The Basics of Setting up the Proper Deadlift Form
- Foot Position: Shins should be as close to the bar as possible, although this varies depending on the type of deadlift you are going to perform. Proper foot placement is a necessity when initiating a deadlift as it allows the weight to be distributed evenly during the lift.
- Breathing: Take deep breaths using your diaphragm to prepare the core muscles of the chest and abdomen. This might seem like a underappreciated task but proper breathing allows the body to prepare and relax in between reps.
- Spine: The spinal column must always be in a neutral position. This not only prevents sustained damage to the spine but also allows for an easier time in lifting weights. Excessively arching your back is sure to end pretty badly as this puts more strain to the back muscles and also the connecting tissues of the spines such as the joints and meninges.
- Hips: The hips should be hinged so the spine can be in a neutral position or keeping the back low and tall. Pushing your hips as far as you can before lowering your body to the bar prepares your muscles for the lift.
- Grip: A good balanced grip is necessary for a great deadlift form. This is achieved by keeping your hands directly under your shoulders or just outside of your hips. Gripping tightly and focusing on the bar around your body to create extra tension in your lats and upper body.
How to Perform a Deadlift
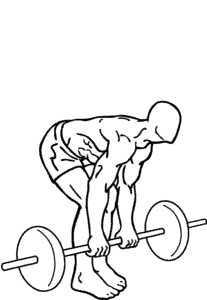 Phase 1
Phase 1
The first phase of the deadlift involves a semi-squat position. This is distinguishable by the squat as the back is partly horizontal to floor level while the weight is placed in the front, whereas in a squat the spine is more vertically inclined to the floor level with the weight placed behind the back.
Phase 2
Involves slowly lifting the weight from the floor to the chest. This must be done using the legs as support and should never be initiated with poor back posture. Additionally, you must also lift using the legs and never your back as this have been known to cause spine injuries.
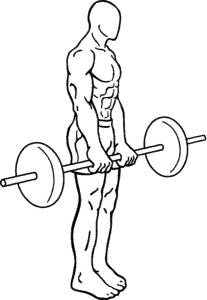 Phase 3
Phase 3
The third phase of the deadlift is simply holding the weight for a few seconds near the pelvic region or pushing it up towards the chest while maintaining a neutral standing position. Then finish it by repeating phase 2 then back to phase 1.
Tips:
Improve Deadlifts: Focused Core Strength Training
A deadlift is considered an advance to intermediate type of exercise which must be planned accordingly as faulty initiation or poor muscle strength have been known to result in injury to the muscle or fractures.
It is highly advised to develop a suitable amount of strength and stability in all muscle groups such as:
- The Upper and Lower Extremities
- It includes the arms, hands, thigh, pelvic muscles and legs.
- The Chest Muscles
- Primarilly involves the pectoralis muscles, deltoid and other muscles connecting the upper extremities to the abdominal muscles.
- The Back Muscles
- The muscles responsible for posture and for keeping the spinal column aligned and well-formed.
- The Abdominal Muscles
- Located in the abdominal area and responsible in distributing the force from the upper extremities and the back.
Developing the muscles of the upper and lower extremities are usually accomplished by training in exercises such as push ups and leg press while the chest muscles by bench presses.
Back muscles includes mostly static muscles and can therefore be enhanced through static exercises such as static and some dynamic body weight exercise.
The abdominal muscles can be effectively strengthened through crunches and balancing exercises.
Improve Deadlifts: Resistance and Balance Training
Muscle stability is the very core of any weight-lifting exercise. In deadlifts a good stable form not only prevents accidents but also strengthen the target muscles through resistance training.
Resistance training improves the strength and stability of core muscles while balance exercises help develop core muscle dexterity and hand-eye coordination. Alternating between the two types of training exercise is beneficial to both stability and mobility.
Resistance exercise is performed using equipment which requires the muscles to resist a certain amount of force such as gravity or weights. Balance exercise is improved by using unstable surfaces such as balance boards, balls, and balance beams to resist being toppling over.
One good example of a balance based sport surfing. When surfing a person needs to balance their weight on the board so that it will not turn over. While balance core exercise seem to be not that useful in deadlifts.
The way the workout works in stabilizing the spine and other muscles is a big plus to any exercise routine. Improving on alternating between balance-based and resistance-based training is a good way to build both core strength and core stability.
This in turn helps in performing deadlifts.